Explore

Stroke is the second leading cause of death globally, with more than 5 million deaths each year2
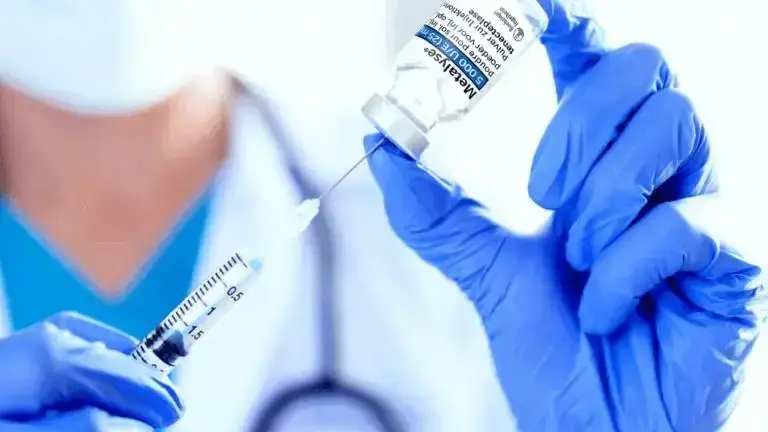
Metalyse® 25 mg is administered by a single IV bolus injection over 5 to 10 seconds1,3-4

Metalyse® 25 mg (tenecteplase) has a similar safety profile to Actilyse® (alteplase)§3

Compared to alteplase, the use of Metalyse® 25 mg is associated with reduction in the utilisation of healthcare resources5-7
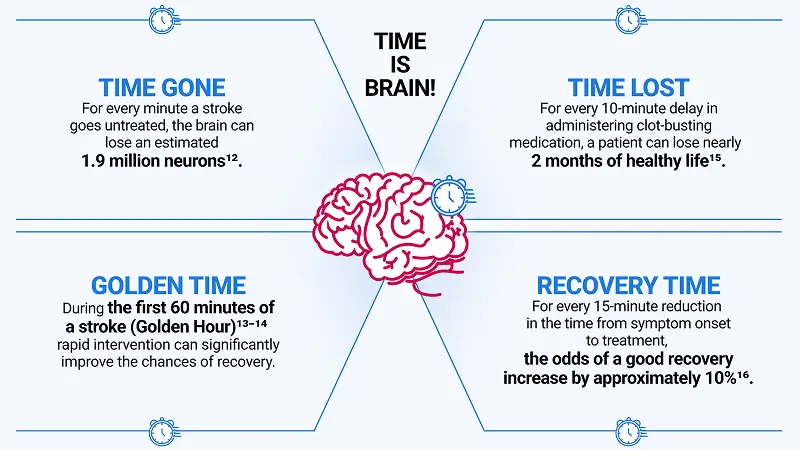
Time is Brain
Stroke affects more than 12 million people each year. It is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Unfortunately, this number is expected to rise because of an ageing global population.8
Acute ischaemic stroke (AIS) occurs when a vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. If blood flow is not restored fast enough, damage to brain cells in a particular area can lead to permanent disability and even death9-11. That’s why when it comes to stroke, every minute matters.

Footnotes
-
CI: confidence interval; IV: intravenous; RD: risk difference; AIS: acute ischaemic stroke.
-
*
Tenecteplase was administrated within 4.5 hours after onset of stroke symptoms, as a weight-tiered bolus dose, based on 0.25 mg/kg for the maximum weight at each tier: < 60 kg, 15 mg tenecteplase; ≥ 60 to < 70 kg, 17.5 mg; ≥ 70 to < 80 kg, 20 mg; ≥ 80 to < 90 kg, 22.5 mg; and ≥ 90 kg, 25 mg.3
-
†
The AcT phase III trial was a multicentre, open-label, parallel-group, registry-linked, randomised trial, in which 1600 patients, presenting within 4.5 hrs of symptom onset, and eligible for thrombolysis, were enrolled from 22 stroke centres across Canada and randomly assigned to tenecteplase (0.25 mg/kg, to a maximum of 25 mg; n=816) or alteplase (0.9 mg/kg to a maximum of 90 mg; n=784). The primary outcome occurred in 36.9% patients receiving tenecteplase and 34.8% patients receiving alteplase (unadjusted RD 2.1% [95% CI -2.6 to 6.9]).3
-
§
In the AcT phase III clinical trial, the rates of AEs were similar for tenecteplase compared to alteplase. The main AEs were: death within 90 days (15.3% for tenecteplase vs. 15.4% for alteplase; RD -0.1 [95% CI -3.7, 3.5]), symptomatic intracerebral haemorrhage (3.4% vs. 3.2%; RD 0.2 [95% CI -1.5, 2.0]), extracranial bleeding (0.8% vs. 0.8%; RD 0.0 [(95% CI -0.9, 0.8]), and orolingual angio-oedema (1.1% vs. 1.2%; RD -0.1 [95% CI -1.1, 1.0]).3
References
-
1.
Metalyse® European Summary of Product Characteristics.
-
2.
Donkor ES. Stroke Res Treat. 2018;2018:3238165.
-
3.
Menon BK, et al. Lancet 2022;400:161-169.
-
4.
Bivard A, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21:520-27.
-
5.
Warach SJ, et al. Stroke 2022;53:3583-3593.
-
6.
Mahawish K, et al. Stroke 2021;52:e590-e593.
-
7.
Warach SJ and Saver JL. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(10):1203-1204.
-
8.
World Stroke Organization, https://www.world-stroke.org/world-stroke-day-campaign/about-stroke/impact-of-stroke.
- 9.
-
10.
Donkor ES. Stroke Res Treat. 2018;3238165.
-
11.
Sacco RL, et al. Stroke 2013;44:2064-2089.
-
12.
Saver JL. Stroke 2006;37:263-266.
-
13.
Saver JL, et al. Stroke 2010;41(7):1431-1439.
-
14.
Advani R, et al. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2017;25(1): 54.
-
15.
Almekhlafi MA, et al. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78(6):709-717.
-
16.
He AH, et al. Int J Stroke 2015;10(7):1062-1067.





